Describe the Inheritance Pattern of Mtdna
The inheritance of mitochondrial and chloroplast genes differs from that of nuclear genes in showing vegetative segregation uniparental inheritance intracellular selection and reduced recombination. A persons nuclear DNA is a patchwork of segments inherited from many different ancestors while a persons mitochondrial DNA is inherited through a single unbroken line of female ancestors.

What Is Mitochondrial Dna And Mitochondrial Inheritance
The three types of Mendelian inheritance are autosomal recessive autosomal dominant and x-linked.

. Although recent evidence has challenged this dogma whole-genome sequencing has identified nuclear-encoded mitochondrial sequences NUMTs that can give the false impression of paternally inherited mtDNA. Due to the maternal pattern of mitochondrial inheritance. Now remember those pathways that are within the mitochondrion for producing energy.
Mitochondrial Genetic Inheritance Pattern. MT-ND5 is a mitochondrial genome coded gene responsible for the protein NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain V protein ND5. The inheritance pattern of mitochondrial DNA means that it can be used to address questions of very deep ancestry.
Refers to dominant genes located on the autosomes. Any child from either a son or a daughter of the affected. Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell.
Which of the following statement correctly describes the inheritance pattern of mtDNA. This DNA is small and circular. Mitochondrial dna mtdna presents several characteristics useful for forensic studies especially related to the lack of recombination to a high copy number and to matrilineal inheritance.
Guidelines for mtDNA Inheritance Mitochondrial DNA mtDNA is found in each cells mitochondria structures that produce ATP the cells main energy source. Lesson Five Using Your mtDNA Test Results. An egg is much larger than a sperm and therefore contains more mitochondria passing its mtDNA to the offspring.
Contribution to the Individuals Fitness. Inheritance Mitochondrial DNA. Most of the cell DNA is in the nucleus in the form of chromosomes or chromatin depending on the level of DNA packing but a small amount of DNA is inside the mitochondria.
How many living relatives could provide mtDNA to test against the mtDNA of the discovered remains that are believed to belong to the missing person shown by a question mark in the pedigree chart. An egg contains mitochondria and a sperm cell does not contain any mitochondria. Both males and females are affected.
One very prevalent pattern of mitochondrial inheritance is uniparental which indicates that in a given cross virtually all the mtDNA in almost all of the progeny comes entirely fromonlyoneofthetwoparentsThispatternisseennearly ubiquitouslyacrosstheanimalkingdomandinmanyplants. Inside the mitochondrion is a certain type of DNA. ND5 is a sub-unit od NADH dehydrogenase a mitochondrial protein.
And it encodes different proteins that are specific for the mitochondrial. Mitochondrial DNA mtDNA or mDNA is the DNA located in mitochondria cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use such as adenosine triphosphate ATP. Thats different in a way from the DNA thats in the nucleus.
Although only females pass on mtDNA to their descendants both males and females have mitochondrial DNA. Table 85e-3 provides a summary of eight illustrative classic mtDNA syndromes or disorders that affect adult patients and highlights some of the most interesting features of mtDNA disease in terms of molecular pathogenesis inheritance and clinical presentation. MtDNA is transcribed from cpDNA outside of the nucleus.
Mitochondrial Inheritance Blank Pedigree PDF Conditions caused by a mutation in the mitochondrial DNA have unusual patterns. Mitochondrial DNA plays important roles in other areas of genetics as well. Which answers accurately describe the inheritance pattern of a woman affected by a disorder caused by a mutation in her mitochondrial DNA hint.
Assume homoplasmy not heteroplasmy and 100 penetrance. 2 answers are correct. The pattern of inheritance that is most likely associated with a mutation in the MT-ND5 gene is.
NDNA is arranged through recombination while transferring to the offspring. Describe the inheritance pattern of mtDNA. If a male has the trait and his spouse doesnt their offspring wont have the trait.
Mitochondrial DNA can reveal information about unique ethnic origins. Mitochondrial genetic mutations in the nuclear DNA can occur in any of the chromosomes. Draw a pedigree illustrating the inheritance pattern.
The first five of these syndromes result from heritable point mutations in either protein-encoding or. Here are some guidelines about how mtDNA. Most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and in plants and algae also.
Sex chromosome and by the number of mutated alleles. The mutant MT-ND5 will be transferred to the progeny. Way it passes generation to generation varies depending on the disease.
Assume all mates are not affected with this same disorder. Vegetative segregation and some cases of uniparental inheritance are due to stochastic replication and partitioning of organelle genomes. If two brothers died in a crash could you use mtDNA to distinguish their remains one from the other.
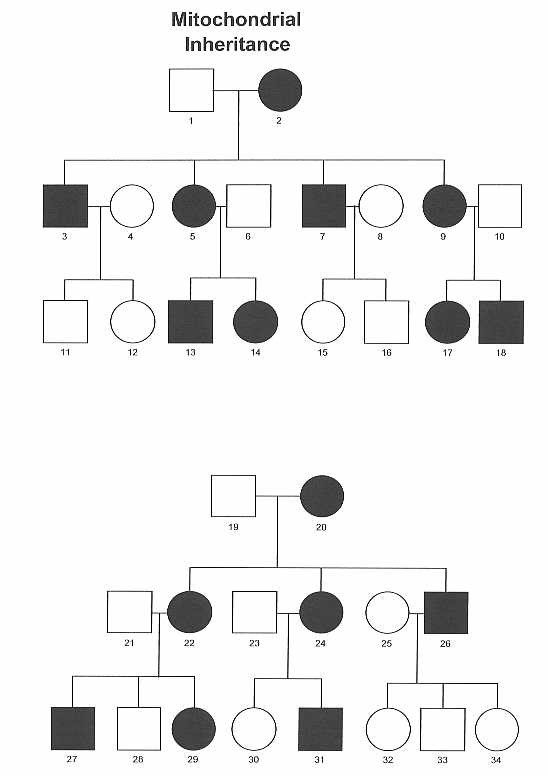
Lesson Two The Inheritance Pattern of mtDNA. MtDNA is maternally inherited. MtDNA is inherited from mother to her offspring without changing.
Mtdna typing based on sequences of the control region or full genomic sequences analysis is used to analyze a variety of forensic samples such as old bones. It has only 16500 or so base pairs in it. As shown in the diagram above the inheritance pattern of mitochondrial DNA is different from that of nuclear DNA.
For many decades it has generally been accepted that mtDNA is inherited exclusively down the maternal line in humans. 1 3 Treatment varies based on the specific type of condition and the signs and symptoms present in each person. NDNA is inherited equally from both parents.
Lesson Three mtDNA Test Results from Family Tree DNA. Lesson One Introduction to mtDNA Testing. Mutations inherited through the chromosomes can be autosomal dominant or recessive AND also sex-linked dominant or.
Mitochondrial inheritance is different from the other genetic inheritance patterns in that it has nothing to do with the chromosomes of the father or the mother. The modes of these inheritances are carried by the genes chromosomal location autosome vs. The condition is transmitted through the female to her offspring.
Those caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA are transmitted by maternal inheritance while those caused by mutations in nuclear DNA may follow an autosomal dominant autosomal recessive or X-linked pattern of inheritance. Different tissues from a mtDNA mutation carrying symptomatic individual can show a wide array of disease pathology from unaffected to affected. Lesson Four mtDNA Results from 23andMe and Living DNA.
Individuals carrying the same pathogenic mtDNA mutations can show a wide array of symptoms from asymptomatic to severely affected.


No comments for "Describe the Inheritance Pattern of Mtdna"
Post a Comment